This is the October 2022 edition of our monthly series of Ethics case studies titled What Do You Think? This series is comprised of case studies from NSPE archives, involving both real and hypothetical matters submitted by engineers, public officials and members of the public.
Your peers and the NSPE Board of Ethical Review have reviewed the facts of the case as shown below. And, here are the results.
Your opinion has been registered for the October 2022 edition of our monthly series of Ethics case studies titled What Do You Think?
Your vote is recorded as:

Want to know how your peers voted? We’ll send you an email with the poll results on October 25.
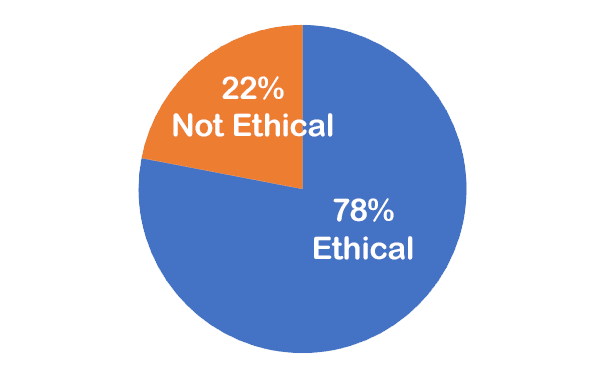
Your opinion has been registered for the October 2022 edition of our monthly series of Ethics case studies titled What Do You Think?
Your vote is recorded as:

Want to know how your peers voted? We’ll send you an email with the poll results on October 25.
A Review of the Facts
Engineer Alice was retained by ABC Manufacturing for the purpose of reviewing documents to form an opinion in a patent litigation matter in an area of Alice’s expertise. Alice performed the requested services and was paid for her work by ABC Manufacturing. Several years later, Alice was retained by Attorney X, who represented a plaintiff in product liability litigation against ABC Manufacturing in a matter not involving any aspect of the earlier patent litigation. Several years later, Alice was again retained by ABC Manufacturing in a different patent litigation matter not related to either of the proceeding events. Alice again performed the requested services and was paid for her work. However, during cross-examination at trial, opposing counsel questioned Alice’s previous relationship both in defense of and in litigation with ABC Manufacturing, implying that by providing those services, Alice was acting improperly.
Was it ethical for Alice to provide services to the parties in the manner described under the facts?
Here is the result of our survey of your peers:
Applicable NSPE Code References:
Code II.4
Engineers shall act for each employer or client as faithful agents or trustees.
Discussion
Over the years, the Board of Ethical Review has considered a variety of difficult cases involving conflicts of interest and the scope of an engineer’s ethical obligation to past and present clients. The Board of Ethical Review has also considered several cases involving the question of engineers providing and performing forensic engineering services and the ethical issues that arise in that context. These cases have involved such issues as performing such services on the basis of a contingency fee, licensure requirements when serving as an expert witness, the qualifications of the individual who is being considered to perform the expert services, relationships with attorneys, and examining the conflict of interest questions that may arise.
As the Board has noted on at least one previous occasion, one of the most common ethical issues that face engineers in their professional lives is the issue of conflicts of interest. At one point in the past, engineering codes of ethics, including the NSPE Code of Ethics for Engineers, specifically implored engineers to avoid all conflicts of interest. The basis for this position was that the engineer could not serve two masters, and when faced with a conflict of interest, the engineer must, in all cases, take steps to remove him or herself from such conflicts. Among the concerns expressed by supporters of this position was that engineers who were involved in the conflict of interest situations created a poor image for the engineering profession because the issue raised the appearance of impropriety.
However, over time, the engineering profession came to the general conclusion that by the very nature of the role of the engineer in society, conflicts of interests were virtually an immutable fact of professional engineering practice and that it was generally impossible for the engineer to, in all cases, remove him or herself from such situations. As a result, codes were changed, and engineers were implored to disclose all known or potential conflicts of interest to their employers or clients, by promptly informing them of any business association, interest, or other circumstance that could influence or appear to influence their judgment or the quality of their services.
After careful review and analysis of the facts and circumstances in the case, we believe the facts do not rise to the level of a conflict of interest prohibited by the Code of Ethics. While engineers clearly have certain basic professional obligations to their employers and clients to protect their interests, engineers do not have a duty of absolute loyalty under which the engineer can never take a position adverse to the interests of a former client. Being a “faithful agent and trustee” to a client does not obligate an engineer to a duty of absolute devotion in perpetuity (See Code II.4). Such an approach would be impractical and compromise the autonomy and professional independence of engineers. This is particularly true in the present case, where the matters at issue are not in any way related to any previous work Alice performed for either of her former clients.
While all engineers must make professional decisions based upon a variety of considerations and factors, engineers must analyze technical matters, weighing all appropriate considerations. For a variety of reasons, some engineers might choose to decline an engagement that could place the engineer in a position adverse to the interests of a former client, even though the engagement is not in any way related to the engineer’s earlier services to the client. However, the Board of Ethical Review is not prepared to say that an engineer who fails to follow this approach is somehow acting in violation of the NSPE Code of Ethics. To do so would undermine the individual judgment, independence, and discretion that each engineer must exercise.
In this connection, the Board is also concerned by the attorney’s implication under the facts that Alice may have acted improperly, with the suggestion that Alice’s action may have constituted a conflict of interest. It appears that the attorney was attempting to draw a parallel between the legal profession, where there is an institutionalized “plaintiff’s bar” and “defense bar” and the engineering profession. However, while engineers may find themselves at times working within the confines of the adversarial legal profession, unlike attorneys, they are not “advocates” in rendering their professional services; they should not be expected to compromise their professional independence and autonomy. While reasonable persons might differ as to whether Alice’s actions under the facts would raise either a conflict or an appearance of a conflict, the Board concludes that a conflict does not exist.
The Ethical Review Board’s Conclusion

It was ethical for Alice to provide services to the parties in the manner described under the facts.
BOARD OF ETHICAL REVIEW
Lorry T. Bannes, P.E., James G. Fuller, P.E., Donald L. Hiatte, P.E., Joe Paul Jones, P.E., Paul E. Pritzker, P.E., Richard Simberg, P.E., C. Allen Wortley, P.E., Chairman
Note – In regard to the question of application of the Code to corporations vis-a-vis real persons, business form or type should not negate nor influence conformance of individuals to the Code. The Code deals with professional services, which services must be performed by real persons. Real persons in turn establish and implement policies within business structures. The Code is clearly written to apply to the Engineer and it is incumbent on a member of NSPE to endeavor to live up to its provisions. This applies to all pertinent sections of the Code. This opinion is based on data submitted to the Board of Ethical Review and does not necessarily represent all of the pertinent facts when applied to a specific case. This opinion is for educational purposes only and should not be construed as expressing any opinion on the ethics of specific individuals. This opinion may be reprinted without further permission, provided that this statement is included before or after the text of the case.









I would understand that the cases be unethical if any of those particular cases had any type of association with each other but they don’t
I disagree with the conclusion. Though neither had any involvement with the other case it would appear there was a conflict of interest.
Years ago I was working for a consulting firm where we represented both developers and municipalities. We could not represent developers in municipalities where we were the municipal engineer. In one instance we worked for a developer already with a project in a municipality that we just retained as a client. We needed to notify the municipality of the conflict and they had to retain a conflict engineer to represent them as deemed a conflict of interest. The firm agreed to the decision. Tough decision but needed to be done
It seems to me that if we have to recuse ourselves from working with clients that we may eventually work on or have worked on either side of a legal issue, we would soon run out of clients to work with. Just disclose anything that may even seem to be connected.
“The good thing about telling the truth is that you never have to remember anything.” Attributed to Mark Twain.
I have served as an expert witness in about a dozen large toxic tort cases. In every engagement I have given the attorneys who retained me the same speech: I will decide how I do my analysis and how I testify. As a practical matter, my testimony was shaped in collaboration with the attorneys, but that shaping was for legal, tactical (e.g. avoiding “sound bites”) and pedagogical (teaching the science and case to a judge or jury) purposes.
In practice, at least in toxic tort cases, experts usually work for either plaintiffs or defendants. In my case I worked solely for plaintiffs, but I would have worked for defendants if they had asked (none ever did) and if they would have consented to my conditions. I would see no ethical issue with doing so, and I think having worked for both “sides” would have increased my credibility.
As an aside, I did not respect the work of several of the experts I opposed—they chose to use outdated analytical techniques that biased results toward their clients’ position. These were issues that we addressed in the litigation, with some success.
The critical information here is that none of the three consulting projects involved the same technology (intellectual property). For a set of three consultations, with three completely different sets of patent claims and design information, the situation is not a conflict.
If, on the other hand, the consultant had been retained numerous times by Company ABC and essentially knew their patent portfolio inside and out, accepting a consultation assignment for an attorney who was suing Company ABC (for any reason – patent infringement or products liability) would definitely give the appearance of a conflict of interest, and might actually become a conflict of interest.
In my practice, at the “conflict check” stage (before a retention occurs) I always inform new clients if I had worked on a consulting project for an opposing party, when that project occurred, and whether the technologies were dissimilar. If I don’t consider the new project a conflict of interest, I inform them of my conclusion, but I suggest they draw their own conclusion about whether they believe the appearance of a conflict is enough for them to find a new consultant.
It is my opinion that dual relationships, of any kind, are unethical.
First, it needs to be stated that no contracts/agreements were signed. These make it clear that one will behave ethically and how. Second, key information regarding disclosures (initial and follow-up) are missing.
Nothing was wrong with the first (of three) interaction. For the second interaction, I think Engineer Alice should have informed both the attorney who contacted her for the product liability case and ABC Company with an explanation justifying the lack of a conflict of interest.
For the third interaction I would do the same, to remind/inform ABC attorneys so they could better do their jobs addressing a potential conflict of interest.
The attorneys that have asked me to be an expert witness have always asked if there was any relationship with the other party in the lawsuit. So that always prevented a conflict of interest for me.